The Growing Importance of Hygiene in Electronics
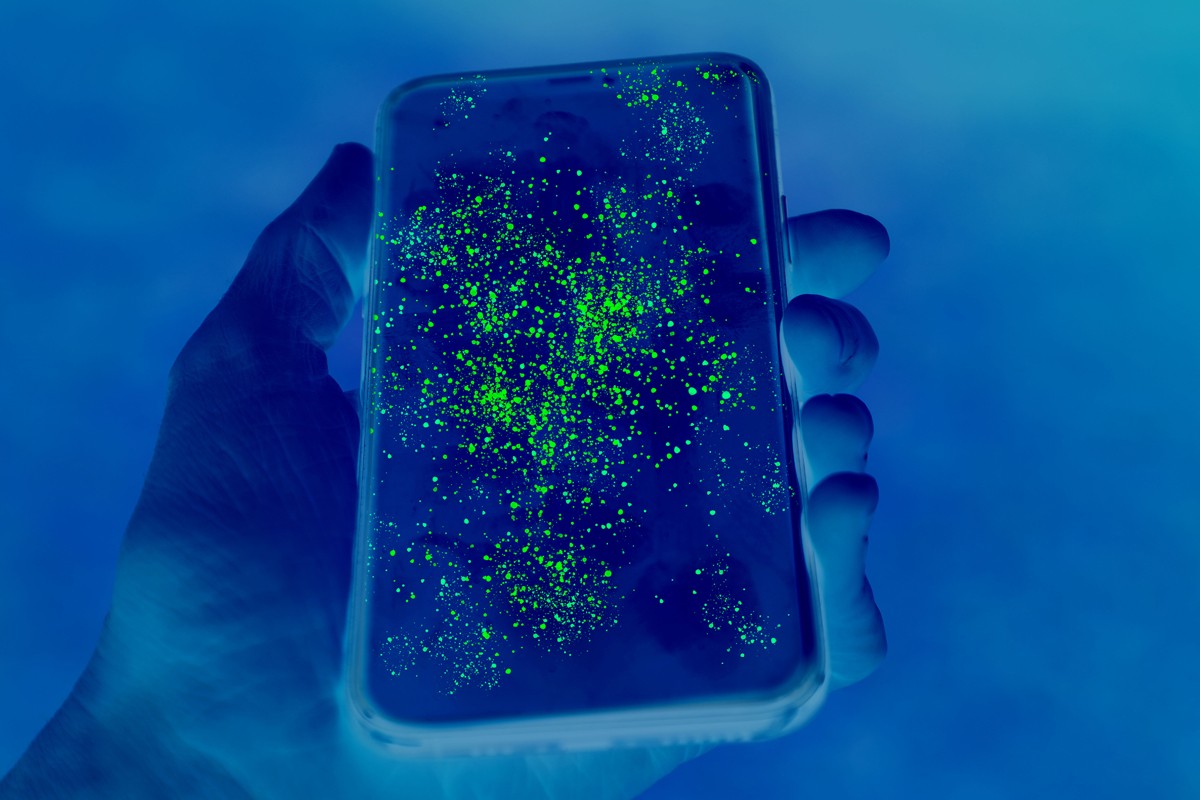

In our ever more interconnected world, electronic devices such as smartphones, tablets, VR headsets, laptops, and keyboards have become indispensable in our daily lives. These devices play important roles both personally and professionally, serving as our communication hubs, entertainment platforms, and workstations. Their ubiquity means they are touched, handled, and carried to various locations, from offices and public transport to kitchens and gyms. This constant use and exposure to these diverse environments make our electronic devices susceptible to microbial contamination.
The extent of the problem is concerning. Research shows that smartphones can harbour up to ten times more bacteria than a toilet seat. This contamination is facilitated by their role as high-touch surfaces, and the warmth generated by the devices, creates a hospitable environment for microbial growth.
Shared devices, often found in workplaces, schools, and healthcare facilities, compound the problem. Keyboards, touchscreens, and other shared electronics often act as vectors for microbial transmission, as they are handled by multiple users without thorough cleaning taking place between uses.
Traditional cleaning methods such as cleaning wipes and disinfectants provide only a temporary solution and are impractical in busy environments. Improper cleaning techniques can also damage sensitive electronic components. The combination of constant use, minimal cleaning, and exposure to various environments underscores the requirement for innovative solutions to mitigate microbial contamination on electronic devices. Addressing this challenge requires a shift in how we perceive device hygiene, moving beyond occasional cleaning to adopting proactive, long-lasting measures such as antimicrobial additive technology, which offers durable, long-lasting product protection without compromising device functionality.
Antimicrobial additive technology is becoming essential for mitigating microbial contamination on electronic devices. They work proactively by targeting microorganisms at a cellular level to inhibit their growth and reproduction. This continuous action is crucial for high-touch devices like smartphones, tablets, and keyboards, which are prone to rapid recontamination even after cleaning.
Technologies such as Biomaster utilise silver-ion technology, an approach that disrupts the biological processes of bacteria. Silver ions interfere with the microbial cell membrane, hinder enzyme activity, and prevent DNA replication, effectively reducing microbial loading on products. This multifaceted mechanism of action ensures robust product protection against a broad spectrum of microbes.
What sets antimicrobial additive technology apart is its durability. Unlike surface disinfectants that lose efficacy as they evaporate or are wiped away, antimicrobial technology is integrated into the material of the device itself, maintaining effectiveness throughout the device’s lifespan. By providing round-the-clock product protection, antimicrobial technology complements traditional cleaning.
The benefits of antimicrobial technology extend beyond individual devices to create a ripple effect of improved hygiene. As a practical, science-backed solution, this technology represents a transformative approach to combating microbial contamination, addressing modern hygiene challenges with efficacy and reliability.
The efficacy of antimicrobial additive technologies is firmly grounded in extensive scientific validation, ensuring their credibility and widespread adoption. Rigorous testing under internationally recognised standards consistently confirms their ability to inhibit microbial growth on treated surfaces. This standardised testing evaluates the antimicrobial activity of treated materials by measuring the reduction in viable microorganisms compared to untreated counterparts. Products like Biomaster have demonstrated exceptional performance in these evaluations, achieving substantial reductions in contamination, even under challenging environmental conditions.
The key element in the effectiveness of technologies such as Biomaster is silver-ion technology, a well-researched and widely utilised antimicrobial mechanism. Silver ions act by disrupting the biological functions of microorganisms through multiple pathways. They penetrate microbial cell membranes, interfering with vital cellular processes, including respiration and nutrient uptake. Additionally, silver ions bind to microbial DNA, inhibiting replication and rendering the microorganisms incapable of survival or reproduction.
There is a significant gap in consumer awareness when it comes to how unhygienic untreated electronic devices are and the potential advantages of antimicrobial additive treatments. While many consumers are familiar with basic hygiene practices, they may not fully comprehend the extent to which electronic devices can harbour bacteria. Consumers may also be unaware that traditional cleaning methods, although effective to some extent, are often short-lived and will not provide long-term protection against microbial growth. As a result, the concept of antimicrobial additive technologies may still seem like an optional or niche feature rather than the essential hygiene solution that it is.
Bridging this awareness gap requires effective education and communication from Additive suppliers such as ourselves here at Addmaster, product manufacturers, and also retailers. Clear, accessible information about the science behind antimicrobial additive treatments, and their real-world benefits can help improve consumers awareness.
As research advances and awareness of hygiene challenges continues to grow, the future of antimicrobial technology holds exciting and transformative possibilities. Ongoing developments in research and innovation are making antimicrobial technology increasingly more effective and essential for maintaining hygiene in our daily interactions with technology. These advancements are on track to become standard features in electronic devices, offering lasting product protection against microbes. With the growing demand for cleaner environments, antimicrobial technology is becoming an integral part of electronics manufacturing, enhancing both the hygiene and functionality of everyday devices.
Looking ahead, the future promises a world where digital interactions are not only about connectivity or productivity, but also about supporting cleaner, more hygienic environments. The devices we rely on every day will play an active role in maintaining hygiene. By integrating antimicrobial technologies, we can ensure that our interactions with technology are not only efficient but also more hygienic.
Further Reading
- Tech Bacteria Experiment: Just How Much Bacteria Is Lurking On Your Devices? https://www.cloudzero.com/blog/tech-bacteria-experiment
- Habyarimana T, Uwizeye C, Munyeshyaka E, Izere C, Mucumbitsi J, Yadufashije C. Bacteriological Study of Electronic Devices Used by Healthcare Workers at Ruhengeri Referral Hospital. Biomed Res Int. 2020 Jun 23;2020:5872929. doi: 10.1155/2020/5872929. PMID: 32685504; PMCID: PMC7330630. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7330630
- Mehdi Nazeri, Javad Salmani Arani, Narjes Ziloochi, Hasan Delkhah, Mohsen Hesami Arani, Esrafil Asgari, Mona Hosseini, Microbial contamination of keyboards and electronic equipment of ICU (Intensive Care Units) in Kashan University of medical sciences and health service hospitals, MethodsX, Volume 6, 2019, Pages 666-671, ISSN 2215-0161, https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2215016119300688
- N.A. Mushabati, M.T. Samutela, K. Yamba, J. Ngulube, R. Nakazwe, P. Nkhoma, A. Kalonda, Bacterial contamination of mobile phones of healthcare workers at the University Teaching Hospital, Lusaka, Zambia, Infection Prevention in Practice, Volume 3, Issue 2, 2021, 100126, ISSN 2590-0889, https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2590088921000147
- Ulger, F., Esen, S., Dilek, A. et al. Are we aware how contaminated our mobile phones with nosocomial pathogens?. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob 8, 7 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-0711-8-7
What Next?
🔗 Follow us on Social Media, here is our LINK TREE
✉️ See how our additive technology can benefit your business by CONTACTING US
🦠 Find out more about Biomaster Antimicrobial Technology HERE
🎥 Watch our video on how Biomaster works WATCH NOW
📰 Subscribe to our Newsletter - SUBSCRIBE
← Back to blog


